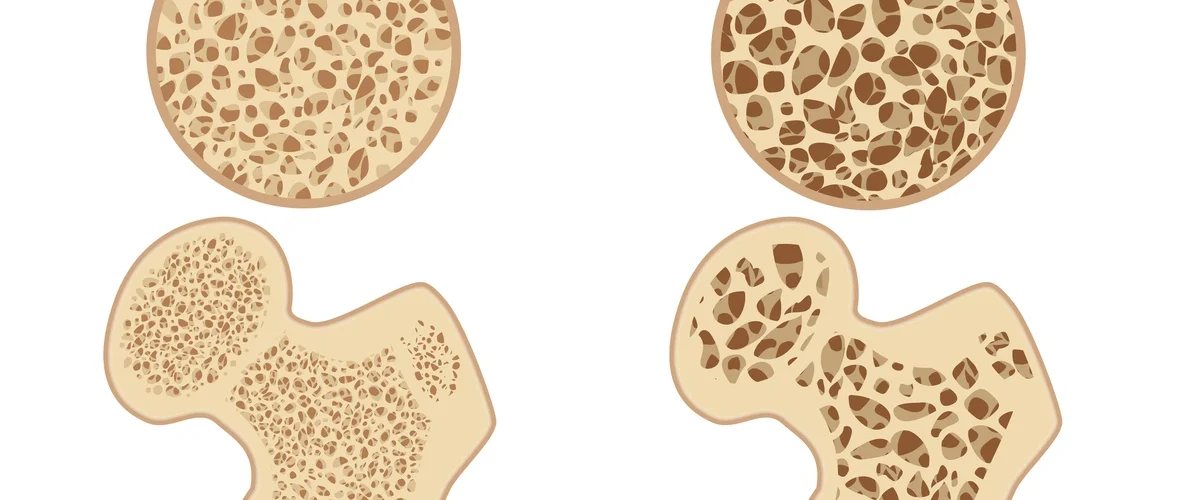
Osteoporosis, a pathological condition characterized by the progressive thinning and weakening of bone matrix, significantly increases the risk of fractures from minimal biomechanical stress. Osteoporosis is a significant public health issue in India, especially among women.
Prevalence and Demographics
Osteoporosis and osteopenia are widespread among Indian women, with notable incidence in the 35-40 age group. Studies indicate that many affected individuals, particularly women, have poor dietary habits and low levels of physical activity. Economic status also plays a crucial role, with women from lower socioeconomic backgrounds being more vulnerable due to limited access to nutrition and healthcare .
Urban-Rural Disparities
There are differences in osteoporosis prevalence between urban and rural areas . Urbanization and associated lifestyle changes like sedentary behavior and unhealthy diets contribute to higher rates . Rural populations may face different risk factors, including limited access to healthcare and education2 . Overall, osteoporosis cases are growing across both demographics, reflecting a broader trend of non-communicable diseases in India .
Causes and Risk Factors
Osteoporosis is influenced by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors .Key risk factors include:
Inadequate nutrition, especially low calcium and vitamin D intake .
Physical inactivity .
Gender differences, with women being more susceptible, especially after menopause .
Unsafe living spaces and inadequate access to nutritious food .
Many people are not aware of the dietary needs for bone strength, and misconceptions exist about the optimal age for building bone density ..
Diagnosis in India
Diagnosing Osteoporosis due to hormonal changes are more likely to go undetected due to lack of awareness about bone health. Women more likely to identify reproductive-related risk factors, similarly men are more aware of lifestyle-related risk factors like smoking and alcohol consumption
Diagnosing osteoporosis typically involves assessing bone density using a Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) scan . This test measures bone mineral density (BMD) at the hip and spine . However, access to DXA scans is limited in resource-limited settings, where alternative methods like the Singh index (using pelvic X-rays) may be used .
Treatment and Management
Effective management relies on lifestyle modifications, including:
- Regular weight-bearing exercises .
- Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D.
- Quitting smoking .
- Limiting alcohol consumption.
- Fall prevention strategies .
Medications such as bisphosphonates, hormone replacement therapy, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), and monoclonal antibodies may be prescribed .
Complications and Prevention
Osteoporosis can lead to fractures, causing pain, disability, and reduced quality of life . Prevention involves maintaining adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, regular exercise, and health screenings for early diagnosis .
Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness is crucial, especially among the elderly and women . Educational campaigns should emphasize the importance of diet, physical activity, and regular screenings . Public knowledge about osteoporosis is limited, particularly in rural areas where diagnostic tools are less available .
Government Policies and Interventions
The Indian government has launched initiatives to address nutritional deficiencies, such as the Poshan Abhiyaan. Corporate entities are also involved in promoting nutrition sufficiency through initiatives like IMPAct4Nutrition. There are recommendations to fortify food with calcium and make calcium supplements more affordable . The government is advised to revise the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for calcium and ensure the availability of supplements at primary health centers.
Urban Health Initiatives
Urban health initiatives, such as the Partnership for Healthy Cities, are essential for tackling osteoporosis and related noncommunicable diseases. These local efforts enhance the health of urban populations and promote awareness